The Best Example of Artarchitecture From the Neolithic Period and Explain Why
Due northeolithic artwork is part of Prehistoric fine art, non but did it serve functional purposes, as is so characteristic of Prehistoric art, only it served aesthetic purposes too. Neolithic art is our visual record of the beginnings of culture. This article will explore the question, "what is Neolithic art?"
Table of Contents
- 1 The New Rock Age: When Was the Neolithic Age?
- 1.ane The Three-Age System
- 1.2 The Neolithic Revolution
- two What Is Neolithic Art?
- 2.one Characteristics of Neolithic Artwork
- 3 Neolithic Artwork
- iii.1 Çatalhöyük
- 3.2 Jericho
- 3.3 Neolithic Megalithic Structures and Artwork
- three.4 Neolithic Pottery and Ceramics
- 4 From the New Stone Historic period to the Contemporary Age
- 5 Frequently Asked Questions
- 5.1 When Was the Neolithic Period?
- 5.ii What Is Neolithic Art?
- 5.3 What Are the Characteristics of Neolithic Fine art?
The New Stone Age: When Was the Neolithic Age?
Before we look at Neolithic art, a brief contextual background of the Neolithic period will requite us more understanding. The Neolithic age was the terminal part of the Stone Age, information technology was besides referred to equally the "New Stone Age". It occurred, approximately, around 10 000 BCE to 3000 BCE.
The word "Neolithic" originates from the Greek words néos pregnant "new" and líthos significant "stone". The English scientist John Lubbock introduced the term "Neolithic" and "Palaeolithic" in the 1870s, the latter of which was the earlier part of the Rock Historic period, too referred to as the "Onetime Stone Age".
In-between the Neolithic and Palaeolithic eras was the Mesolithic Stone Historic period, meaning "Center" Rock Age.
The Three-Age System
The Stone Age falls into the broader categorization of prehistoric times, and then let us briefly zoom out and encounter where nosotros are. The Iii-Age System, started in the 19th Century, was utilized as an archaeological dating tool to categorize prehistory into iii respective periods, namely, the Stone Age (c. ii.6 million years ago to 3000 BCE), the Bronze Age (c. 3000 BCE to 1300 BCE), and the Iron Age (1300 BCE to 900 BCE).
This categorization made information technology easier for not but archaeologists and scholars, simply anyone who seeks to understand the history and evolution of man. Although there were other scholars that introduced a divisionary system for prehistory, the Danish man Christian Jürgensen Thomsen, the Director of the Royal Museum of Nordic Antiquities, refined this method of classification.
 Portrait of Christian Jürgensen Thomsen (1788-1865);See page for writer, CC Past ii.0, via Wikimedia Eatables
Portrait of Christian Jürgensen Thomsen (1788-1865);See page for writer, CC Past ii.0, via Wikimedia Eatables
He outlined this organisation in 1837 in one of his essays, titled, Kortfattet Udsigt over Mindesmærker og Oldsager fra Nordens Fortid (1837) ("Brief Outlook on Monuments and Antiquities from the Nordic Past"). This essay was part of a collection of volumes published by the Danish Royal Guild for Ancient Nordic Manuscripts, this was titled, Ledetraad til Nordisk Oldkyndighed (1836) ("Guideline to Scandinavian Antiquity").
Thomsen's method was pregnant because he categorized unlike materials from prehistoric times, namely, stone, bronze, and iron.
Additionally, these unlike periods existed in dissimilar parts of the earth. For example, some of the primary Neolithic regions were Mesopotamia, the Levant, North Africa, Asia, and Western and Northern Europe, among others. The time periods also ranged between regions.
The Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic period marked the beginnings of changes in civilization, this has been referred to every bit the Neolithic Revolution. This term was introduced by the Australian archaeologist, Vere Gordon Childe in the early on 1900s. Childe's usage of the term "revolution" could have possibly come from the tenets of Marxism, which influenced him.
Information technology is of import to note that most of the changes during these prehistoric periods occurred gradually – it was not an overnight occurrence. The nomadic lifestyle was yet prominent and with steady progression, farming increased, which led to settlements. Childe'south concept of a "revolution" too received critique from various archaeologists because it may have been "misleading".
 A short animation of the chronology of the introduction of agriculture in Europe;Wikirictor, CC By-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
A short animation of the chronology of the introduction of agriculture in Europe;Wikirictor, CC By-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
From the hunter-gatherer mode of living there were new developments in farming and agronomical modes of living. During the Palaeolithic period, people utilized rock and bone tools, but these were basic in their form. Artwork existed during this period, but information technology was also rudimentary, fabricated from natural materials and pigments.
The Mesolithic menses slowly became more developed with polished tools as well as the beginnings of agriculture and settlements. This then became the Neolithic menstruation, where settlements were permanent, people farmed, grew grains, domesticated animals, and various abode-based functions like weaving, pottery, and sewing. This certainly was a "revolutionary" type of menstruation in man evolution because it gear up the foundations for humans to settle and alive in more permanent environments.
This type of living, compared to the nomadic lifestyle, inevitably changed human being behaviors and in turn, information technology afflicted all areas of life, including art and what information technology was made for.
What Is Neolithic Fine art?
As we discussed above, the Neolithic flow vicious somewhere between 10 000 BCE to 3000 BCE. It marked the showtime of numerous new developments in social and cultural life. In clarifying the Neolithic art definition, we volition talk over various related characteristics beneath.
 Geometrical scratched motive near Hodmezovasarhely, Hungary, Neolithic menstruation;Takkk, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Eatables
Geometrical scratched motive near Hodmezovasarhely, Hungary, Neolithic menstruation;Takkk, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Eatables
Characteristics of Neolithic Artwork
The characteristics nosotros outline for Neolithic art are quite different from the type of characteristics we outline for art movements like the Renaissance. Neolithic fine art, first and foremost, served several functions, either related to food, farming, ritual, ornamentation, or any other purpose related to Neolithic living.
Furthermore, Neolithic art was non a split aspect of the various Neolithic cultures, so we volition besides look at cultural characteristics, which inform the artwork.
The major changes that took place during this fourth dimension were notably the increased security in terms of safety and food. With this came an increase in population and people settled in communion or "small tribes". This likewise gave people the sense of place and territory, which inevitably increased the manner they treated their surround, for case, living spaces, tools, objects, and each other.
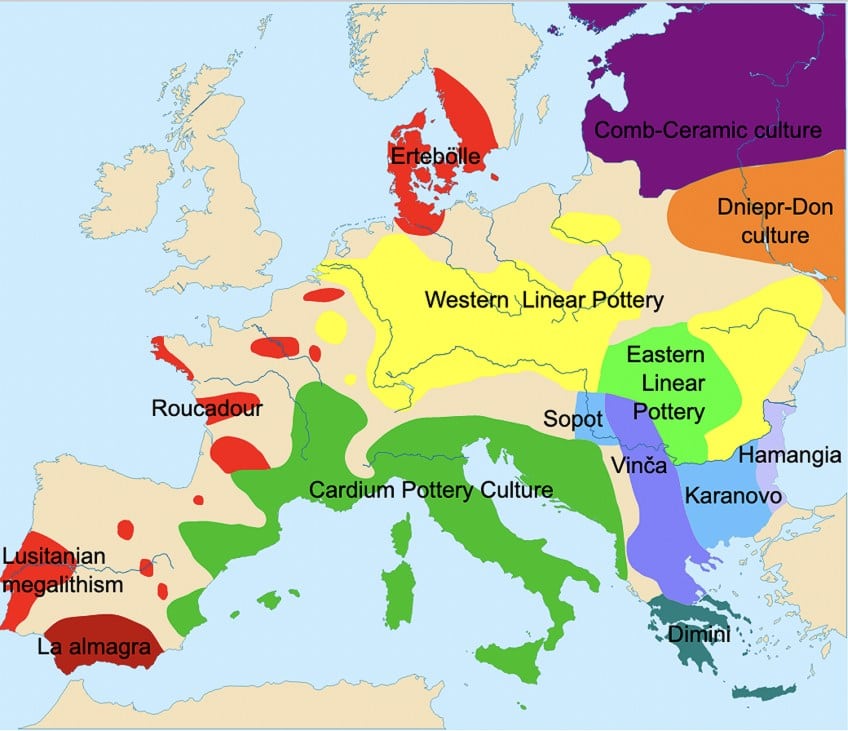
 Map of the dissimilar cultures and settlements of the European Centre Neolithic menses; !Original: w:Sugaar (talk | contribs);westward:Clarifer (talk | contribs)Vector: Joostik, CC By-SA three.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Map of the dissimilar cultures and settlements of the European Centre Neolithic menses; !Original: w:Sugaar (talk | contribs);westward:Clarifer (talk | contribs)Vector: Joostik, CC By-SA three.0, via Wikimedia Commons
This follows on from how people treated one another, there was an increase in hierarchical structures. Nutrient was also unremarkably maintained and stored on a more communal level instead of individually in households. Furthermore, at that place were also areas for rituals, which were evidently tied to the veneration of crops and climate changes.
There was a focus on the feminine and masculine qualities, and nosotros volition discover this in the Neolithic sculpture of female figurines throughout these periods.
Cults and shamanism were as well a office of cultures and certain animals held more than meaning than others. The realm of religion and ritual during prehistoric times is circuitous, and information technology is important to note the vastness of it throughout the regions and the importance placed on different deities and conceptions of the divine.
Neolithic Artwork
Neolithic artwork consists mostly of pottery, terracotta sculptures, statuettes, diverse smaller pieces that were utilized equally adornments, Neolithic drawings like engravings and wall paintings, pictograms, and nearly notably megalithic structures – call up Stonehenge (we will get to that). Neolithic sculpture was as well made through new techniques like sculpting it from dirt and baking it instead of just strictly through carving.
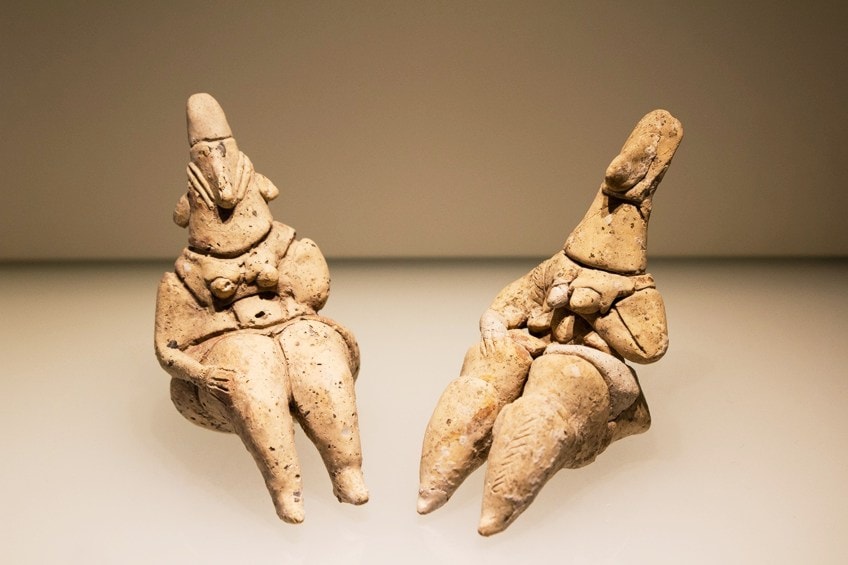 Neolithic Yarmoukian culture figurines at the Israel Museum in Jerusalem;Oren Rozen, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Eatables
Neolithic Yarmoukian culture figurines at the Israel Museum in Jerusalem;Oren Rozen, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Eatables
Below, we discuss some of the prominent creative pieces, from pottery, skulls, to megalithic structures. We will besides discuss important archaeological sites where extensive collections of artworks were found, giving united states of america a visual indication of the part art played in the Neolithic communities.
Bear in mind that while this only touches on a select few examples of Neolithic artwork, at that place are significant numbers of artwork excavated from this art flow.
Çatalhöyük
Çatalhöyük is also referred to as Çatal Höyük and is an archaeological site in Turkey not far from one of the major cities named Konya. The site was deemed a UNESCO Globe Heritage Site in 2012. It is a site filled with evidence of not only hunter-gatherers but people who settled and lived in communities. It is reported that effectually 6000 to 8000 people inhabited these spaces thousands of years ago.
The site consists of diverse buildings made of mud bricks, these were built very closely adjacent to one some other, in fact, people moved around via the rooftops and entered their respective living spaces through holes or doors in the roof, some doors were also on the sides, past means of ladders or stairs.
 A very big Neolithic and Chalcolithic proto-metropolis settlement in southern Anatolia, 7400 BC;Murat Özsoy 1958, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
A very big Neolithic and Chalcolithic proto-metropolis settlement in southern Anatolia, 7400 BC;Murat Özsoy 1958, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The walls inside the homes were ordinarily plastered and rooms are reported to have been kept in tidy atmospheric condition. Additionally, in that location were too upwards to 2 rooms in a dwelling with an extra room that could accept been utilized for storage purposes.
There has also been a various range of art discovered on this site, such as murals on walls inside and exterior homes.
The bailiwick affair for these murals was generally geometric patterns and figural shapes. The figural shapes were ofttimes of animals with some human-like forms incorporated. An case of this is titled the Neolithic Wall Painting in Edifice eighty, Çatalhöyük, among many other such images.
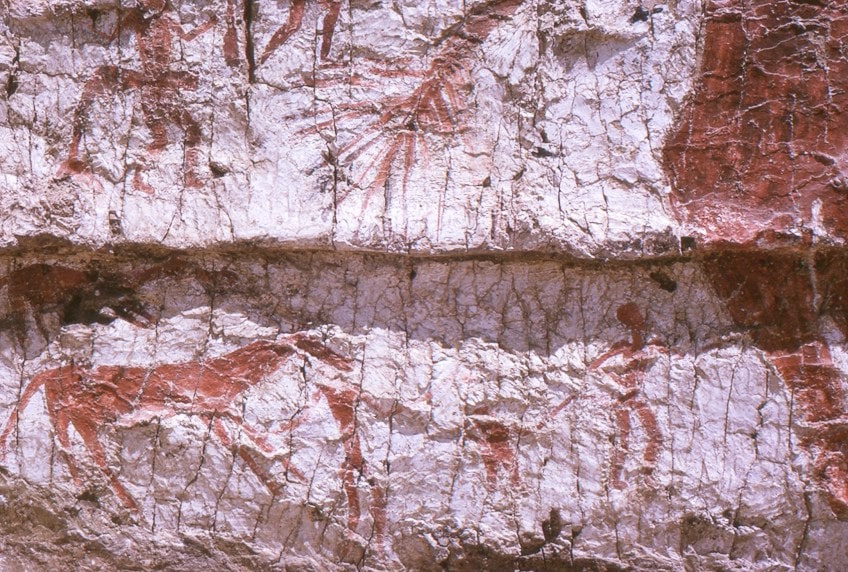 Detail of a Çatalhöyük landscape showing the hind part of the aurochs, a deer, and hunters;Omar hoftun, CC BY-SA three.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Detail of a Çatalhöyük landscape showing the hind part of the aurochs, a deer, and hunters;Omar hoftun, CC BY-SA three.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Some examples of this include vultures at a dead corpse and what appears as two cranes faced towards each other with a fob backside them. A characteristic stance or delineation of these figures has been described as "splayed" because we will often discover their heads not depicted or they would have no hands or feet.
Female clay figurines have also been institute on the site, for example, the popular Seated Woman of Çatalhöyük (c. 6000 BCE). This depicts a female sitting between two feline figures, perchance two armrests with the heads of feline figures. Some sources propose she may as well be sitting on the feline figures. It is not clear what feline figures these are – it could perchance be leopards, lionesses, or panthers. The figurine is made of baked dirt and the right armrest and caput have likewise been restored.
The figurine is currently housed at the Museum of Anatolian Civilizations, located in Ankara city, Turkey.
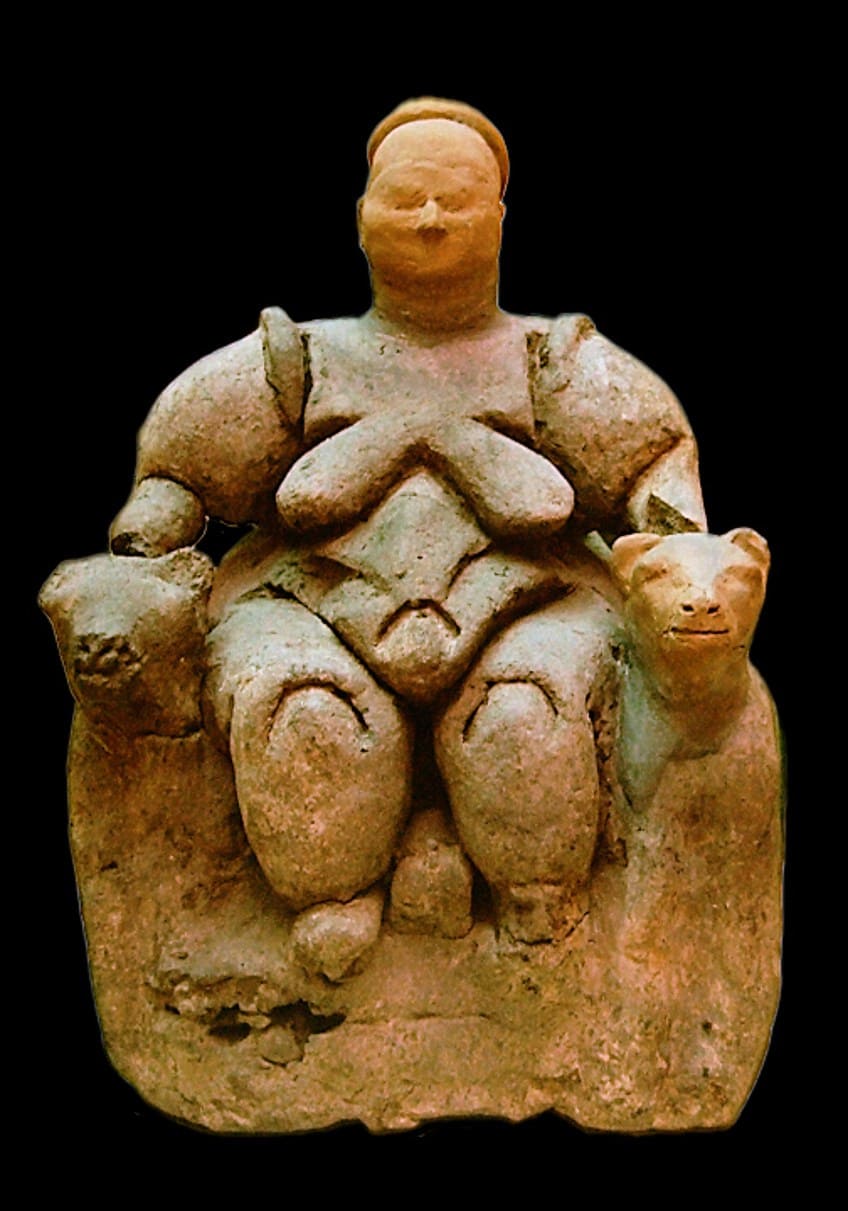 Seated Woman of Çatalhöyük, Museum of Anatolian Civilizations, Ankara, Turkey;User:Roweromaniak, CC Past-SA 2.v, via Wikimedia Commons
Seated Woman of Çatalhöyük, Museum of Anatolian Civilizations, Ankara, Turkey;User:Roweromaniak, CC Past-SA 2.v, via Wikimedia Commons
These female figurines were pop forms of Neolithic and connected to female deities, still, at that place has been debate over the importance of the female deities compared to male person deities, and sources too point out that both genders had equal standing. Furthermore, there take been around 2000 figurines excavated, predominantly consisting of animals.
The figurines were as well found in different areas of homes, for example, some were found in garbage pits, others in walls or floors. The purpose of these figurines could be for skilful luck or to keep bad spirits at bay. The above-mentioned Seated Woman of Çatalhöyük was excavated from a grain bin.
The excavator, James Mellaart, suggested that her purpose was related to good harvests and the rubber of food supplies.
Jericho
The Palestinian city, Jericho, is another site where the Jericho Skull (9000 to 6000 BC) and other similar skulls have been found. What is unique about these skulls is that they are plastered human skulls. Many were males, withal, there were also females and children.
The skulls are believed to exist connected to ritual and religious practices of burial the dead. When people died, they were buried under the floors and their skulls would often exist plastered with shells placed in the remaining eye sockets and sometimes human features like pilus would be painted on them.
 A plastered skull from the ancient city of Jericho in Palestine 7000 BC;Mary Harrsch, CC BY two.0, via Wikimedia Eatables
A plastered skull from the ancient city of Jericho in Palestine 7000 BC;Mary Harrsch, CC BY two.0, via Wikimedia Eatables
There are other sources that advise the skulls were for the "practice of headhunting" in which case they would exist "trophies". Other suggestions indicate the skulls were to venerate the dead ancestors or to remember passed away loved ones by having an "image" of them (in this case, their skull) plastered and decorated to appear more life-like. The skulls were establish at many other sites besides, for example, Nahal Hemar, Tell Ramad, Beisamoun, Kfar Hahoresh, and others.
The exact reason for these skulls is varied, but from what the evidence suggests, these are early examples of what is believed to exist portraiture in art.
Neolithic Megalithic Structures and Artwork
As nosotros motion on from the Neolithic sites mentioned above, nosotros move into what is probably ane of the most fascinating aspects of Neolithic art: Neolithic megaliths. These are found in numerous regions of the world, and many are famously known in the regions of Europe like England and Ireland.
Stonehenge
Stonehenge (c. 2550 to 1600 BCE) is in England, on Salisbury Apparently, Wiltshire. It is one of the biggest prehistoric structures constructed, consisting of numerous large stones bundled in a circumvolve; there is an outer circle and inner circumvolve. The outer circumvolve consists of stones standing vertically each with a horizontal lintel stone. The stone is made from sarsen stone, which is a prevalent sandstone in England.
The stones stand around 13 anxiety alpine, measure to around seven feet in width, and weigh over 20 tons each.
Inside this ring are five sarsen trilithons (a trilithon is a structure consisting of two vertical stones next to the other with a horizontal stone on top of both), these appear in a horseshoe shape and weigh around 50 tons. We will also see diverse Bluestones inside the outer and inner circle of sarsen stones.
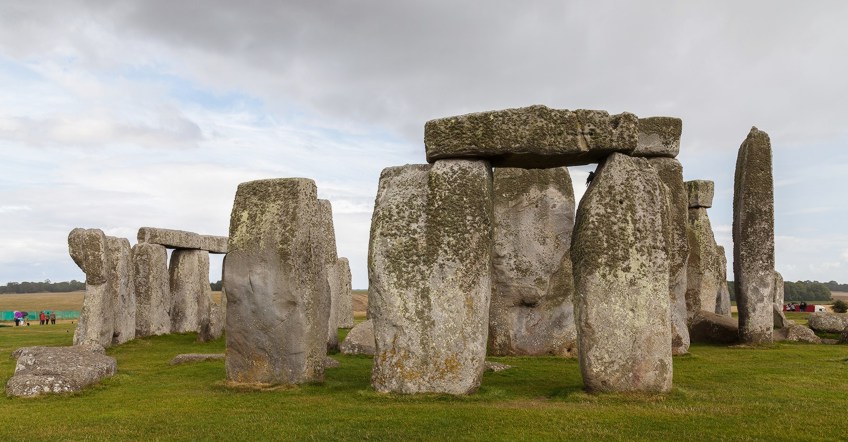 Stonehenge, Wiltshire, England; Diego Delso, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Stonehenge, Wiltshire, England; Diego Delso, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Stonehenge was reportedly built in three phases, although in that location is debate about the accurateness of when the phases took place. Phase One was around 3100 BCE, Stage Two was effectually 3000 BCE, and Stage Three was effectually 2600 BCE, this was likewise the longest phase and lasted until around 2400 BCE.
This was a awe-inspiring undertaking and in that location is however a lot of contend most how this ancient structure was erected and by whom.
As to the function of Stonehenge, information technology possibly served religious and formalism purposes. Its orientation is towards the sunrise on the Summer Solstice, which gives a further indication for its purpose. Information technology was declared a UNESCO Globe Heritage Site in 1986.
Avebury
There are besides other rock monuments in the surrounding regions, for example, the Avebury monuments in Wiltshire, England. These are three stone circles located around the Avebury village. It is also role of a henge, a bank with a ditch, surrounding the stones. The outer circle measures 1088 feet and the inner circle of rock measures around 322 anxiety on the northern side and around 354 feet on the southern side.
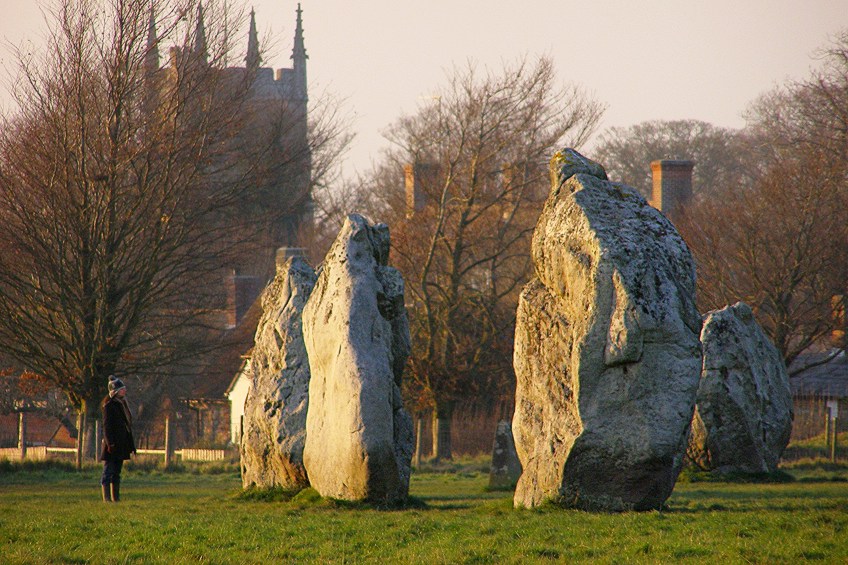 Avebury stones in the South Circle viewed from the south-east quadrant bank. From left to right, stones 103, 102, 101, and 105 are shown. The small concrete post marks the position of missing rock number 104. The belfry of St James church building is in the groundwork;JimChampion, CC By-SA iii.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Avebury stones in the South Circle viewed from the south-east quadrant bank. From left to right, stones 103, 102, 101, and 105 are shown. The small concrete post marks the position of missing rock number 104. The belfry of St James church building is in the groundwork;JimChampion, CC By-SA iii.0, via Wikimedia Commons
It was congenital approximately around 2850 BCE to 2200 BCE. This is function of the associated World Heritage Sites, of which Stonehenge is a office. There is also a broad debate about the construction of Avebury as well every bit its purpose. Many scholars and non-scholars accept posed ideas as to this construction's purpose, some say it was most likely for ritual and ceremonial purposes.
Brú na Bóinne
Brú na Bóinne, meaning "Palace of the Boyne" or "Valley of the Boyne", is in the County Meath, Ireland. It is besides referred to as the Boyne Valley Tombs. It includes the three major burial mounds or passage tombs, namely, Newgrange (c. 3300 to 2900), Knowth (c. 3200 BCE), and Dowth (between 3200 to 2900 BCE).
These are located nearly the River Boyne and are around 40 to 50 kilometers north of the metropolis of Dublin. The site was declared a UNESCO Earth Heritage site in 1993. The Brú na Bóinne circuitous is home to numerous Neolithic henges, stones, tomb chambers, mounds, and other structures related to ceremony and ritual.
An interesting fact about the Brú na Bóinne circuitous indicates that it was built before the Pyramids in Egypt.
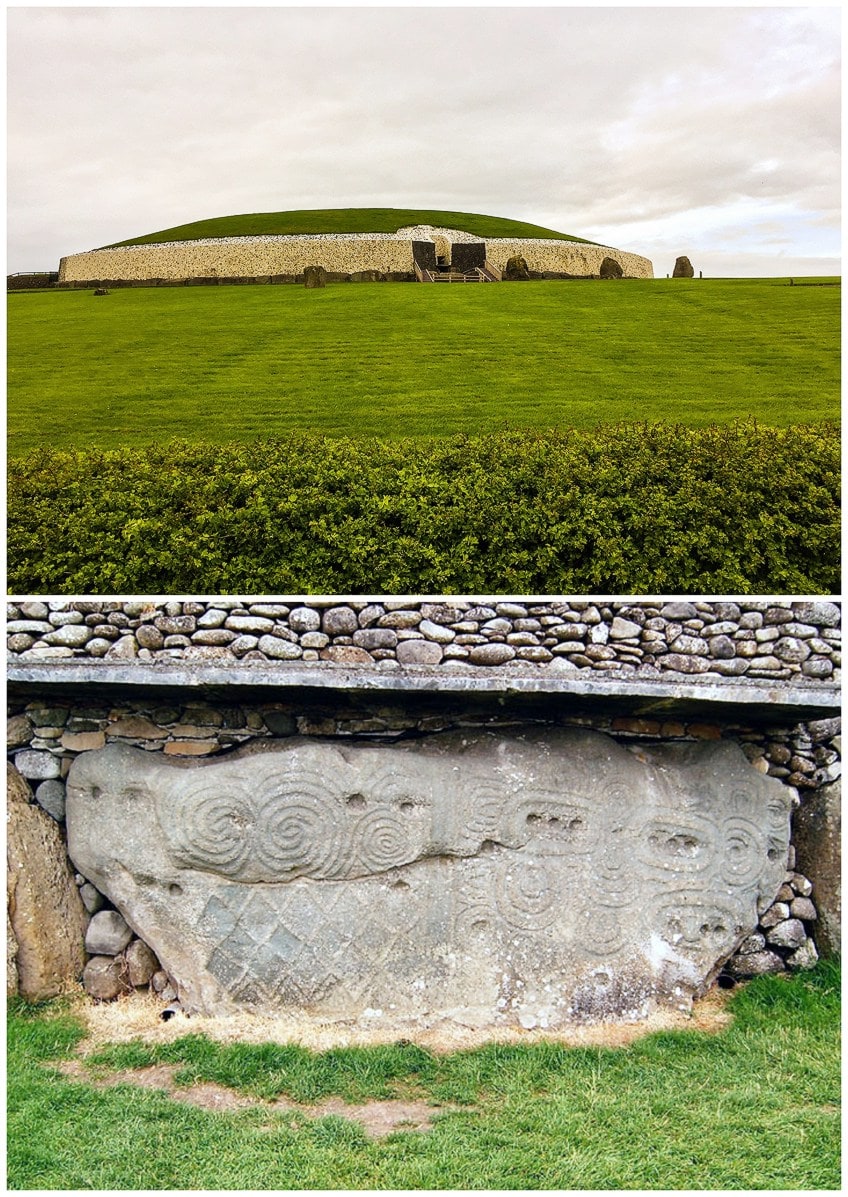 TOP: The Neolithic passage tomb of Brú na Bóinne in Newgrange; Dieglop, CC By-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons | Lesser: A detail of one of the Neolithic borderstones of Brú na Bóinne, Newgrange; Pasztilla (régi), CC BY-SA three.0, via Wikimedia Eatables
TOP: The Neolithic passage tomb of Brú na Bóinne in Newgrange; Dieglop, CC By-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons | Lesser: A detail of one of the Neolithic borderstones of Brú na Bóinne, Newgrange; Pasztilla (régi), CC BY-SA three.0, via Wikimedia Eatables
We will also notice the all-encompassing noesis and application of astronomy, such as the Newgrange mound and its passage. The mound (measuring 249 anxiety wide, or beyond the structure, and 39 feet in top) was built with layers of stone and earth with a passage leading around 60 anxiety into the central part within the mount. The passage inside the chamber is aligned when the lord's day rises in the Wintertime Solstice. The chamber inside is lit up for an estimated time of 17 minutes.
Another important aspect of these mounds is their Neolithic rock art or rock engravings.
These are significant examples that tell united states about the Neolithic period art in Ireland. In that location are geometric motifs in singled-out patterns, namely, spirals, circles, arc-like forms, chevrons, various lines like parallel lines, lozenges, and radials.
The triple spiral or "triskele" shape is amid one of the mutual shapes we encounter on Irish megaliths. At that place is wide fence among scholars about the purpose of these designs, some say they are symbolic while others say they are decorative.
Neolithic Pottery and Ceramics
There were four periods that categorized Neolithic pottery and ceramic production in the Middle East, in the Mesopotamia region. These were namely, the Hassuna period (c. 7000 to 6500 BCE), the Halaf period (c. 6500 to 5500 BCE), the Ubaid period (c. 5500 to 4000 BCE), and the Uruk period (c. 4000 to 1300 BCE).
The Hassuna period was named later on the archaeological site called Tell Hassuna in Iraq.
It was the site where the Neolithic Hassuna culture lived. The pottery from this site has been divided into three phases, namely, Hassuna Archaic, Hassuna Standard, and Samarran. The characteristics of pottery include creamy coloring with incised patterns.
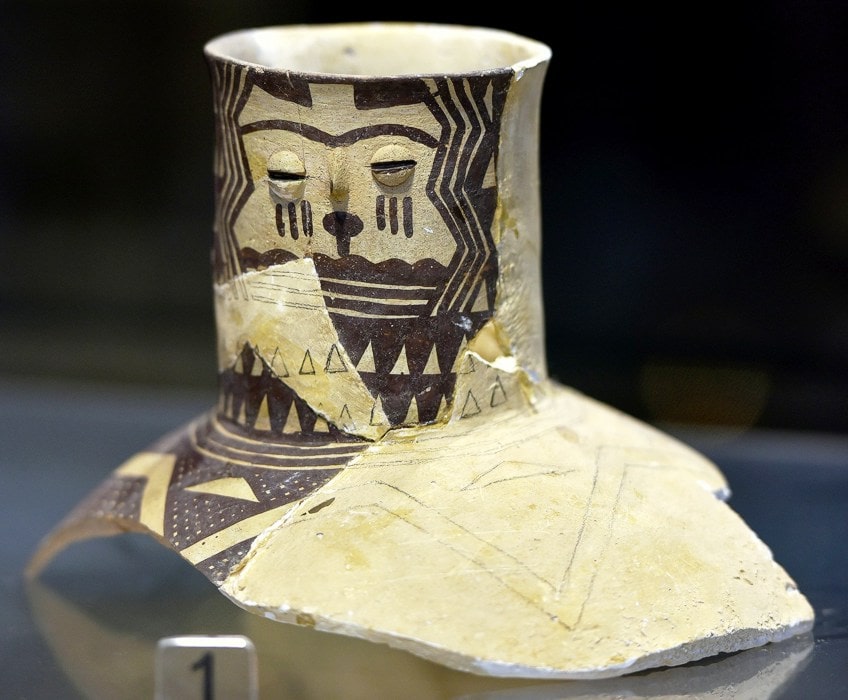 A pottery fragment showing the cervix of a bottle-shaped jar painted with a adult female's face. The eyes and nose were added. The overall depiction points to Samarra culture from Tell Hassuna, 5000 BCE;Osama Shukir Muhammed Amin FRCP(Glasg), CC By-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
A pottery fragment showing the cervix of a bottle-shaped jar painted with a adult female's face. The eyes and nose were added. The overall depiction points to Samarra culture from Tell Hassuna, 5000 BCE;Osama Shukir Muhammed Amin FRCP(Glasg), CC By-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The Halaf flow was named after Tell Halaf in Syria. Characteristics of pottery included a wider range of colors with animal and geometric patterns. Halaf pottery has been considered quite technically advanced in its production.
When nosotros look at the Ubaid menses, which is named after the archaeological site Tell al-'Ubaid located in Ur in Iraq. Pottery during this period also had flossy and dark-brown colors with patterns that consisted of zig-zags, chevrons, and other geometric motifs. Pottery was likewise characterized as much plainer during this period.
The final Uruk period that occurred was named after Uruk, a urban center in Sumeria.
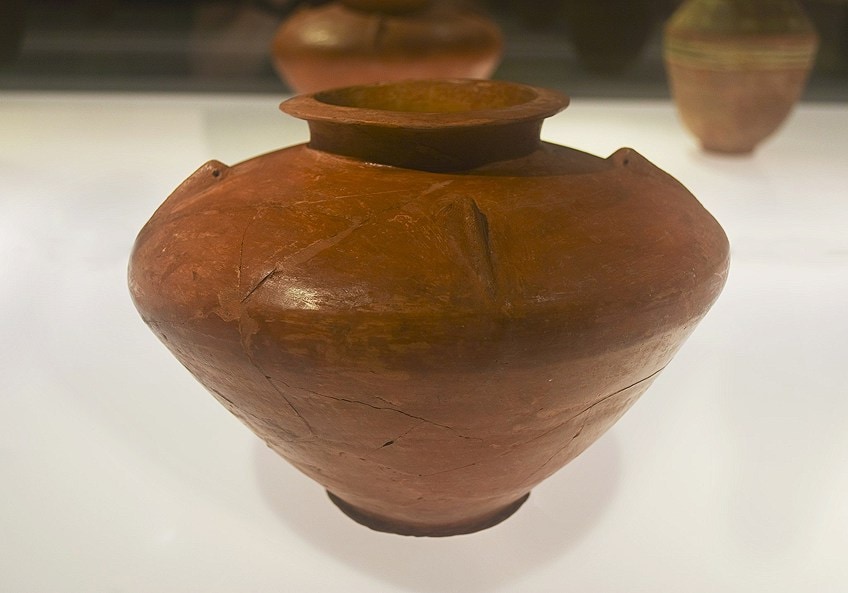 Pottery vessel from the late Susa Two period (Uruk Menses), 3300-3100 BC, Chogha Mish, Khuzestan Province, Iran;Jerónimo Roure Pérez, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Pottery vessel from the late Susa Two period (Uruk Menses), 3300-3100 BC, Chogha Mish, Khuzestan Province, Iran;Jerónimo Roure Pérez, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The potter's wheel made it easier to produce pottery. Kilns were also enhanced. Pottery during this period appeared more than monochrome with lesser decorative motifs on the containers. If at that place were decorations these would announced as what is known as "lozenge" motifs. There was also a large collection of pottery from this period in a range of shapes and sizes suited to different foods and needs. The various jars and vases had big bellies (bodies), shorter necks, and larger openings or mouths.
Neolithic pottery and ceramics in China were functional in nature and had various characteristics as the Neolithic flow progressed.
During the earlier Neolithic catamenia, pottery was fabricated from earthenware and fired mostly in bonfires, and these were a red colour. Pottery was as well hand-made through the coiling method. Jugs were more prominent during the middle Neolithic menstruum in Prc, for example, the amphorae.
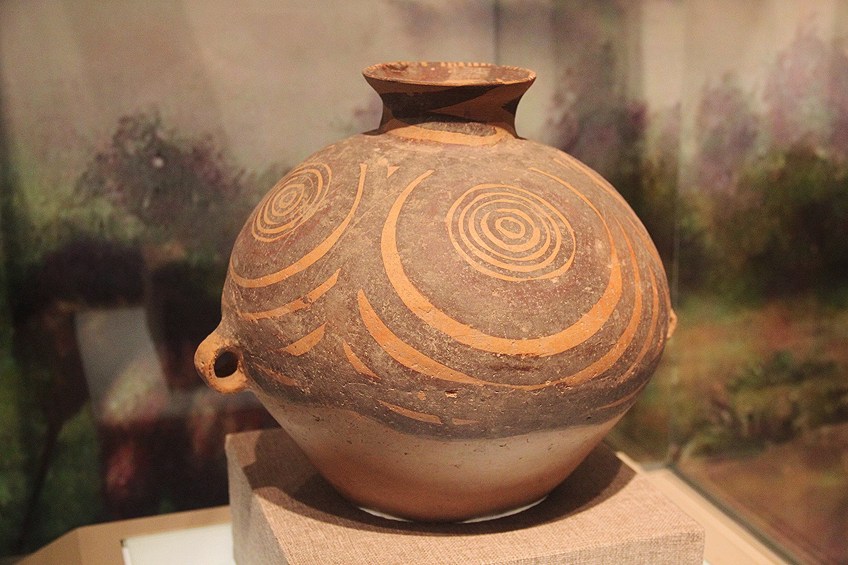 A typical example of Neolithic pottery in China, Xinyang Urban center Museum, Henan Province; Gary Todd, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
A typical example of Neolithic pottery in China, Xinyang Urban center Museum, Henan Province; Gary Todd, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
These were likewise ruddy in color and had various incised patterns. In other regions of Prc, some pottery was black in color due to it being charcoal-tempered. The after Neolithic periods in China were increasingly burnished and decoratively painted with geometric patterns. At that place were many different Chinese cultures throughout the Neolithic period and the product of pottery and sculpture developed in unique and complex ways.
There were also various cultural and social factors that allowed this Neolithic art to evolve and become refined not only as a utilitarian object but equally a grade of craftsmanship.
From the New Stone Historic period to the Gimmicky Age
The Neolithic or New Rock age evolved into the Statuary historic period, which started with the advent of more people using bronze. It started around 3300 BCE and lasted until around 1200 BCE. There was a broad range of artwork, not to mention extensive statuary carvings, merely ceramics too developed more aesthetically. Records of the get-go blazon of writing have been institute from this age too.
 LEFT: Tablet of the Epic of Gilgamish (Obverse side); Stephen Langdon, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons | Right: Tablet of the Epic of Gilgamish (Opposite side); Stephen Langdon, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
LEFT: Tablet of the Epic of Gilgamish (Obverse side); Stephen Langdon, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons | Right: Tablet of the Epic of Gilgamish (Opposite side); Stephen Langdon, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Nosotros will also find the Stone age revived in our contemporary historic period through various artists who replicate the enormity of Neolithic megaliths in everyday objects, for instance, creative person Mark Leckey'due south GreenScreenRefrigeratorAction (2010).
Other examples of or "throwbacks" to Neolithic times tin can exist viewed in land art from the 1970s, for example, Nancy Holt's installations called Sun Tunnels (1976). These structures, 4 physical cylinders, were erected in Utah'south Great Bowl Desert and align with the Summer and Winter Solstice'south sunrise and sunset, reminiscent of the astronomical and ceremonial qualities we encounter from the Neolithic period art.
The Neolithic period was vast and complex, spanning across many regions, consisting of many peoples who all gradually evolved from the hunter-gatherer lifestyle to a more settled lifestyle including farming and agronomics, and beast domestication. We can almost say the Neolithic age gear up the stage for how nosotros live today, in communities and settled environments.
Ofttimes Asked Questions
When Was the Neolithic Period?
The Neolithic age occurred, approximately, around x 000 BCE to 3000 BCE. Information technology was the final part of the Rock Age, otherwise the "New Rock Age". The word "Neolithic" originates from the Greek words néos pregnant "new" and líthos meaning "stone". The Paleolithic historic period preceded the Neolithic historic period.
What Is Neolithic Art?
The Neolithic catamenia art varied in style and subject field matter, it too occurred in numerous regions worldwide. It consisted of pottery, Neolithic sculpture, statuettes frequently of female and male figures, but including animals too. There were as well Neolithic drawings like engravings and wall paintings as well as rock art on various structures, most notably megalithic structures like Stonehenge or Newgrange. Neolithic pictographs were also mutual and many sources state that these could have been the precursors of writing.
What Are the Characteristics of Neolithic Art?
Neolithic fine art served unlike functions, these were either related to nutrient, farming, ritual, decoration, or any other purpose related to the Neolithic lifestyle. Neolithic art was not a separate part of Neolithic cultures, the two go together, for case, the style people alive straight influenced the Neolithic fine art definition and its characteristics. The changes that took place during this time included increased security like personal prophylactic and food. These changes resulted in increased populations, which gave people a sense of identify and territory, this also changed the way people treated their surround, for case, living spaces, tools, objects, and each other.
Source: https://artincontext.org/neolithic-art/
0 Response to "The Best Example of Artarchitecture From the Neolithic Period and Explain Why"
Post a Comment